October 08, 2024
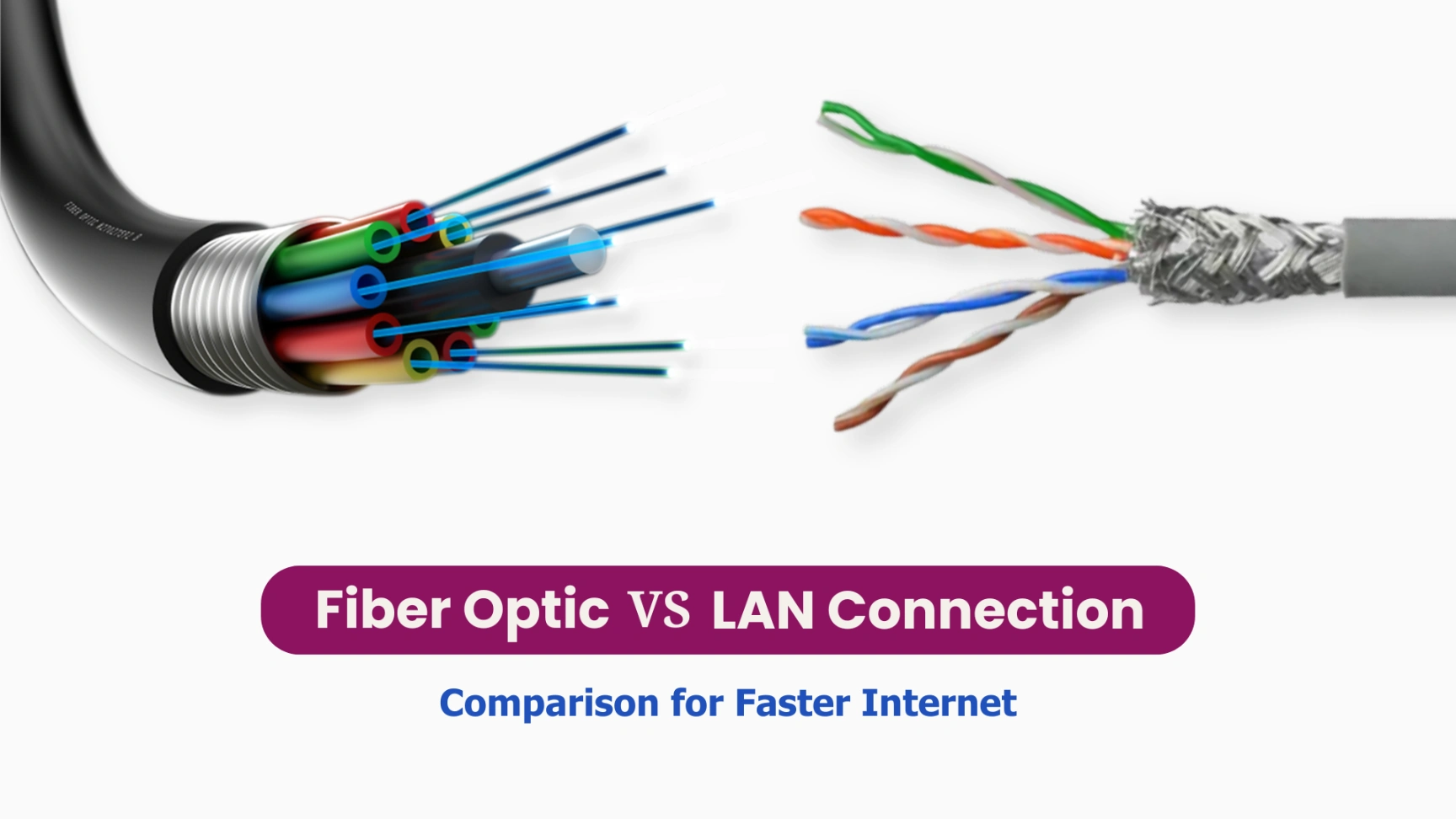
Fiber Optic vs. LAN Connection: Comparison for Faster Internet
The internet connection you choose is an important decision because it determines the speed, reliability, and capacity you can rely on. Among some other options available today, Fiber Optic and LAN connections are two of the most commonly used, each with its own strengths and characteristics. Whether for work, entertainment, or daily tasks like video conferencing, streaming, or cloud computing, your connection needs to keep up with modern demands.
In this article, we’ll explore the differences between Fiber Optic and LAN connections, examining their strengths in speed, reliability, and capacity. By understanding how each option works and weighing their pros and cons, you can make an informed choice that best suits your home or business needs in today’s digital world.
What is a Fiber Optic Connection?
Imagine the internet is like a super-fast highway, and your data, things like videos, messages, and games, are like cars zooming down that highway. Now, if you want those cars to get to their destination as quickly as possible, you need the best road. That’s where Fiber Optic Internet comes in.
Fiber Optic Internet is a special way to send data using light. It travels through super-thin strands of glass or plastic, called optical fibers. Think of these fibers like tiny see-through tubes where light zips through at incredibly high speeds, where data travels as flashes of light. To put it in perspective, data in fiber optics moves at about 70% of the speed of light. This is why fiber internet can be so fast. It can reach speeds of up to 10 Gbps (gigabits per second).
However, just like even the best highway can have some bumps, fiber optics can sometimes face small issues with signal loss over long distances. But overall, it’s one of the best ways to get super-fast and reliable internet.
What is LAN Connection?
Imagine you’re at home and you want all your devices like your computer, smartphone, and smart TV to be able to connect and communicate with each other. That’s where a LAN Connection comes in.
LAN stands for Local Area Network. It’s a network that connects devices in a specific area, like your house, school, or office. These devices can be connected through Ethernet cables, which are like sturdy wires that link each device to a central hub, usually a router.
But LANs aren’t just about cables. You can also connect to a LAN wirelessly using Wi-Fi. For example, in your home, the router is connected to the internet through an Ethernet cable. This router then sends out Wi-Fi signals, allowing all your devices to join the LAN without needing to plug in any cables.
So, whether you’re sharing files between computers, streaming a movie on your smart TV, or connecting your smartphone to the internet, all these devices can be part of the same LAN, making it easier to share and access resources within your home.
How Does Fiber Optic Connection Work?
Fiber optic cables are incredibly thin, about the same width as a human hair, ranging from 125 to 250 microns. These cables are made of glass or plastic and transmit light signals instead of electrical ones. Inside the cable, there’s a tiny central part called the core, where the light travels. Around the core is a special layer called cladding that helps keep the light bouncing inside the core so it can travel a long way without losing much signal. This bouncing of light is called refraction.
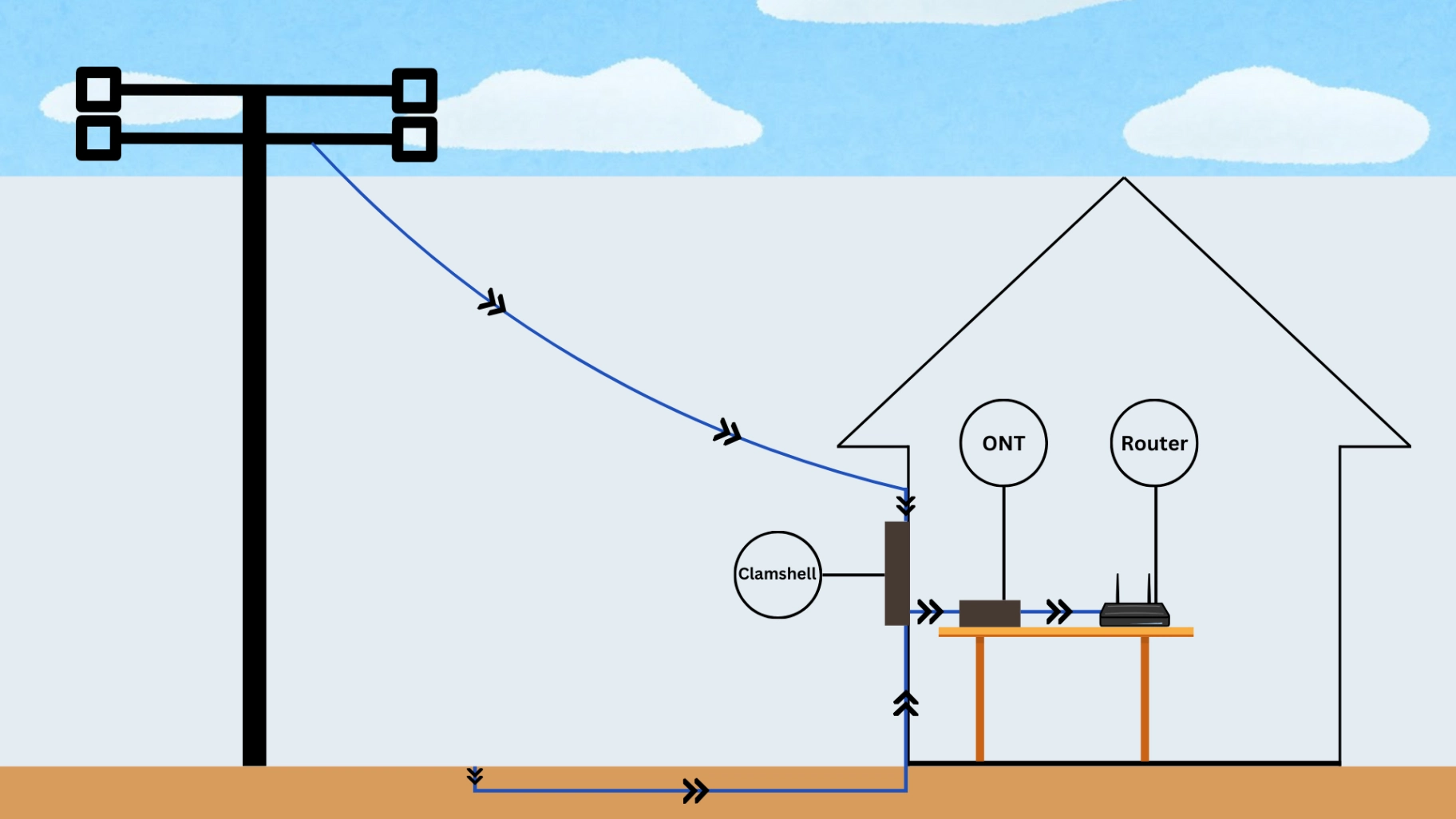
To protect these delicate components, fiber optic cables are often housed in a protective casing known as a clamshell. The clamshell not only shields the cables from environmental damage but also provides structural support, ensuring that the fibers inside remain intact and undisturbed. This is especially crucial during installation and maintenance, where the cables might be exposed to harsh conditions or rough handling.
The light in these cables flashes on and off really quickly, much like Morse code, where different flashes carry different pieces of information. The faster these flashes happen, the more data can be sent. At each end of the fiber optic cable, there are devices called transmitters and receivers. The transmitter sends the light signals, and the receiver picks them up and turns them into data you can use, like videos or web pages.
To keep the light signals strong over long distances, optical amplifiers are used. These devices boost the signals so they don’t weaken too much. Routers and switches manage and direct the data to make sure it gets to the right place. Distribution points are where the cables split off to connect to different homes or buildings.
Finally, at your home or office, devices like fiber modems or Optical Network Terminals (ONTs) connect the fiber optic cables to your internet devices, allowing you to go online. The entire system, from the core to the clamshell, works together seamlessly to provide fast, reliable internet service.
Fiber Optic vs LAN: Pros and Cons
Fiber Optic Connection
Pros:
1. High Speed: Fiber optic internet is capable of transmitting data at extremely high speeds, often reaching up to 10 Gbps. This means you can download files, stream high-definition videos, and play online games with minimal lag and buffering.
2. Long Distance: Unlike traditional cables, fiber optic cables can transmit data over long distances without significant loss of quality. This is because light signals travel through the glass or plastic fibers with very little attenuation, making fiber optics ideal for long-range data transmission.
3. Stability: Fiber optic connections provide superior stability compared to traditional cables. Due to their immunity to environmental factors like electrical interference and weather conditions, fiber optics ensure a consistent and reliable connection, minimizing downtime and fluctuations in speed. This makes fiber optic networks ideal for businesses and homes where uninterrupted internet access is crucial.
4. Bandwidth: Fiber optic technology offers a large bandwidth capacity. This means it can handle a high volume of data and support multiple devices simultaneously without a drop in performance. Whether for a busy office or a household with many connected devices, fiber optics can manage heavy data traffic efficiently.
5. Interference: Fiber optic cables are immune to Electromagnetic (EM) interference, which means they maintain a stable connection even in environments with high electrical noise. This is because they transmit data as light rather than electrical signals, which are less susceptible to interference.
6. Security: Fiber optic cables offer enhanced security since they do not emit electromagnetic signals. This makes them less vulnerable to eavesdropping and data breaches, as intercepting data transmitted through fiber optics is much more difficult compared to traditional cables.
Cons:
1. Cost: The initial cost of installing fiber optic connections is higher than that of traditional copper cables. This includes the cost of the fiber cables themselves, as well as the specialized equipment needed for installation and maintenance.
2. Specialized Equipment: Setting up and maintaining fiber optic networks requires specialized equipment and trained professionals. This means that not all service providers or technicians are equipped to handle fiber optics, potentially leading to higher service costs.
LAN Connection
Pros:
1. Cost-effective: LAN (Local Area Network) connections, which use traditional copper cables, are generally less expensive to set up and maintain compared to fiber optics. This is because copper cables and associated equipment are widely available and less costly.
2. Ease of Installation: LAN networks are straightforward to install. Ethernet cables, commonly used in LAN setups, are easy to run and connect to devices, and the installation does not typically require specialized skills or equipment.
Cons:
1. Bandwidth: LAN connections often have lower bandwidth compared to fiber optics. This can result in slower internet speeds, especially when multiple devices are connected and consuming significant amounts of data simultaneously.
2. Limited Speed: Traditional LAN connections using copper cables can’t match the high speeds offered by fiber optics. As technology has advanced, the limitations of older LAN technology have become more apparent, especially for high-speed data requirements.
3. Limited Distance: Copper cables used in LAN networks are less effective over long distances. Signal quality can degrade, leading to slower speeds and potential data loss the farther the signal has to travel from the source.
4. Latency: LAN connections, particularly those with older copper cables, may experience higher latency. This means there can be noticeable delays in response times, which can affect real-time activities such as online gaming and video conferencing.
5. Security Vulnerabilities: LAN networks can be more susceptible to security issues. Copper cables can be more easily tapped or intercepted, increasing the risk of data breaches compared to the more secure fiber optic connections.
6. Interference: Copper cables in LAN setups are prone to electromagnetic interference and signal crosstalk, which can affect network performance. Proper shielding and installation are required to mitigate these issues and maintain a reliable connection.
.webp)
Which Is Better? Optical Fiber or LAN Connection?
Before diving into the specifics, it's important to understand why fiber optic is often the preferred choice over traditional LAN connections. Both technologies serve the purpose of delivering the internet, but they differ significantly in terms of performance, reliability and future potential.
The following comparison table outlines key metrics such as speed, bandwidth, stability, and security to help you make an informed decision.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
By examining this table, it becomes clear why fiber optic technology is frequently the superior choice for internet connectivity.
Related Blog: What is the Difference Between Dedicated Internet vs Shared Internet Connection?
Conclusion
In today's tech-driven world, a high-speed and reliable internet connection is essential for businesses of all sizes. Fiber optic internet has significantly transformed how both consumers and businesses operate. It supports modern needs such as video conferencing and cloud computing, which are commonplace in today’s office environments.
Moreover, technology extends beyond traditional computing devices to include IoT (Internet of Things) devices. At home, activities like streaming services such as Netflix and Chorki, and online gaming, also benefit from the high-speed connectivity that fiber optic technology provides.
Fiber optic internet not only meets the demands of contemporary business operations but also enhances everyday digital experiences, making it a crucial element for both professional efficiency and personal enjoyment.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between Fiber Optic and LAN connections?
- Fiber Optic connections use light signals transmitted through glass or plastic fibers, offering incredibly high speeds and long-distance data transmission with minimal signal loss. LAN (Local Area Network) connections, on the other hand, typically use copper cables to transmit electrical signals, which can result in lower speeds and reduced effectiveness over long distances.
2. How does the installation process for Fiber Optic internet work?
- The installation process for Fiber Optic internet typically involves running fiber optic cables from the service provider's network to your home or office. These cables are usually installed underground or along existing utility poles. Once the fiber optic cable reaches your location, a technician will install an Optical Network Terminal (ONT) to convert the light signals into data that your devices can use. The ONT is then connected to a router or modem, allowing you to access the internet.
3. Why is Fiber Optic internet faster than LAN connections?
- Fiber Optic internet is faster because it transmits data as light signals through optical fibers, which can carry large amounts of data at high speeds—up to 10 Gbps. LAN connections using copper cables transmit data as electrical signals, which are slower and can degrade over long distances.
4. How much more reliable will Fiber Optic internet be compared to my previous connection?
- Fiber optic internet is far more reliable than local area network (LAN) connections. While LAN setups rely on internal wiring within a building, they still depend on the quality of the main internet source. Fiber optic technology delivers faster, more stable speeds directly to your location, and is not affected by interference or signal degradation over long distances. This ensures a consistent connection, making fiber much more reliable than LAN connections that may experience slowdowns due to external factors.
5. Is Fiber Optic internet better for gaming and streaming?
- Yes, Fiber Optic internet is better for gaming and streaming due to its high speeds and low latency, which reduce buffering and lag. It can handle the demands of high-definition streaming and online gaming, providing a smoother experience compared to traditional LAN connections.